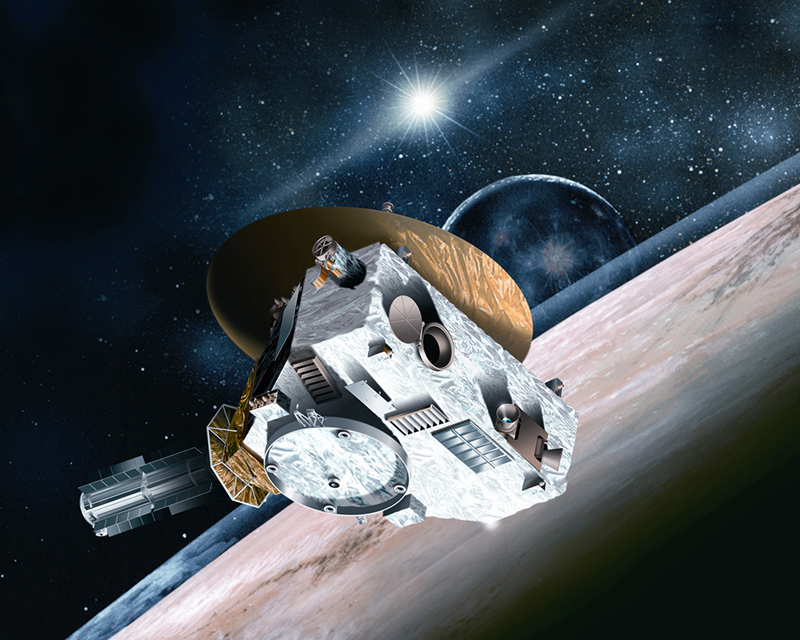
Chandra Looks to Pluto
On July 14th, the New Horizons spacecraft will fly by Pluto during its unprecedented mission to the outer Solar System. In addition to the data gathered by New Horizons and its suite of instruments, other telescopes – including the Chandra X-ray Observatory – will be pitching in to help astronomers learn more about this distant and icy world.
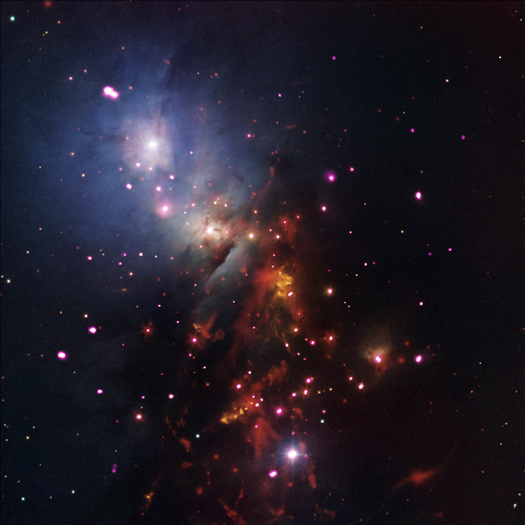
Stellar Sparklers That Last
While fireworks only last a short time here on Earth, a bundle of cosmic sparklers in a nearby cluster of stars will be going off for a very long time. NGC 1333 is a star cluster populated with many young stars that are less than 2 million years old, a blink of an eye in astronomical terms for stars like the Sun expected to burn for billions of years.
Bat Astronomy: Echolocation of a Neutron Star

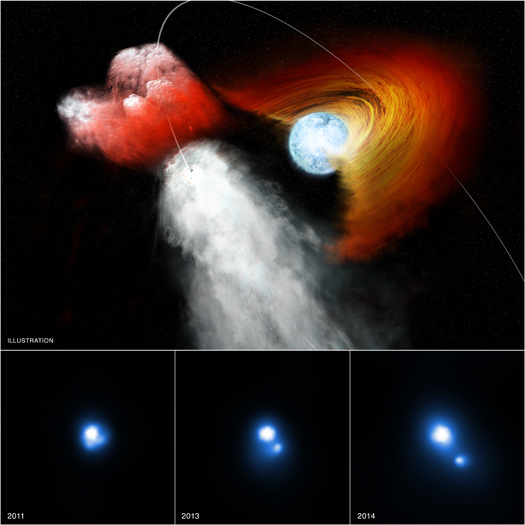
We are pleased to welcome guest blogger Sebastian Heinz, a Professor in the Astronomy Department at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Sebastian led the team that discovered light echoes around Circinus X-1, the subject of our latest press release. He received his Ph.D. at the University of Colorado at Boulder. He studies relativistic jets − a phenomenon observed around black holes and neutron stars and started investigating the neutron star Circinus X-1 star when he was a Chandra Postdoctoral Fellow at MIT.
Some astronomical discoveries are straightforward − you observe something and it is immediately clear what you have found and what the consequences are. Often, though, astronomy requires the combination of different people’s skills and different kinds of data to solve a puzzle. This was definitely one of those puzzles.
When we downloaded the data from our long Chandra observation of the neutron star Circinus X-1 in early 2014, it was immediately clear that we were looking at an exceptionally bright light echo. Light echoes are created just like sound echoes, when light waves bounce off an obstacle (in this case dust clouds). Because their path has a kink in it, the bounced light waves take longer to arrive at the telescope than the waves that didn't bounce. Our echo resulted from a two-month long huge X-ray outburst Circinus X-1 had had in late 2013 (see the X-ray movie from MAXI included here), making it the largest, brightest, most spectacular set of X-ray rings to date, which is why we jokingly call Circinus X-1 the "Lord of the Rings".
X-ray Echoes Pinpoint Location of Distant Flaring Neutron Star
Data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory has helped provide a rare opportunity to determine the distance to an object on the other side of the Milky Way galaxy, as described in our latest press release
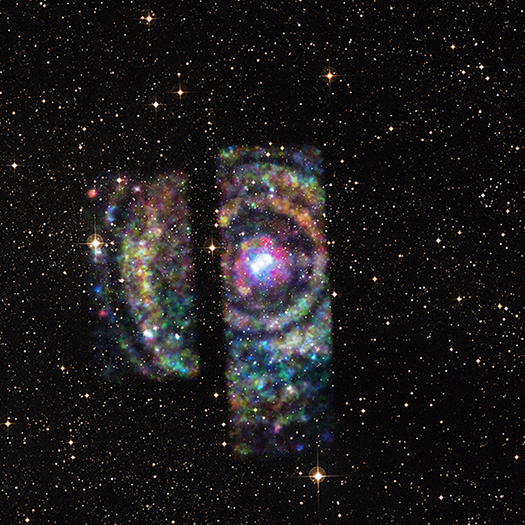
Chandra Finds Evidence for Serial Black Hole Eruptions
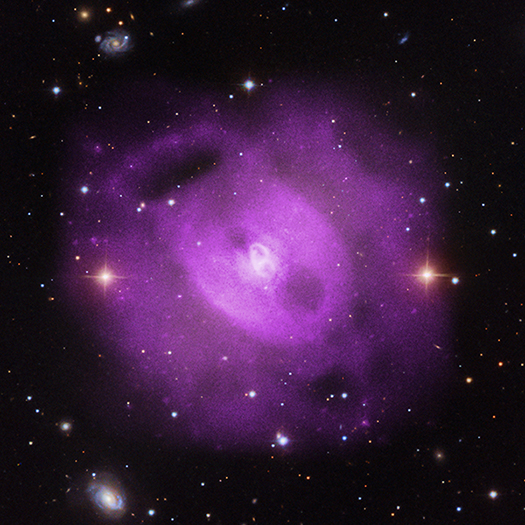
Astronomers have used NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory to show that multiple eruptions from a supermassive black hole over 50 million years have rearranged the cosmic landscape at the center of a group of galaxies.
Scientists discovered this history of black hole eruptions by studying NGC 5813, a group of galaxies about 105 million light years from Earth. These Chandra observations are the longest ever obtained of a galaxy group, lasting for just over a week. The Chandra data are shown in this new composite image where the X-rays from Chandra (purple) have been combined with visible light data (red, green and blue).
The Great and the Small: Is Quantum Foam Losing its Fizz?

Eric Perlman
We are very pleased to welcome Eric Perlman as a guest blogger today. He led the study setting limits on the foaminess of space-time that is the subject of our latest press release. Eric is a professor at the Florida Institute of Technology. After completing his PhD in 1994 at the University of Colorado, he held postdoctoral fellowships at the Goddard Space Flight Center and Space Telescope Science Institute. He also held research positions at Johns Hopkins University and the University of Maryland, Baltimore County. He has lived in Florida for 8 years and enjoys his family, singing, and playing chess and other board games.
Astronomy has been a tool of discovery since the dawn of civilization. For thousands of years, humans used the stars to navigate and find their place in the universe. Astronomy made possible the travels of the ancient Polynesians across the Pacific Ocean as well as measurements of the Earth’s size and shape by the ancient Greeks. Today, astronomers search for hints about what the universe was like when the universe was much younger. So imagine, for a second, what life would be like – and how much less we would know about ourselves and the universe – if the microscopic nature of space-time made some of these measurements impossible.
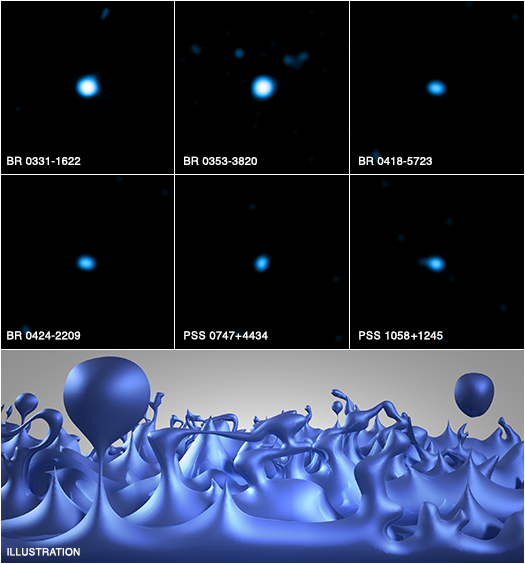
NASA Telescopes Set Limits on Space-time Quantum Foam
A new study combining data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and Fermi Gamma-ray Telescope, and the Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array (VERITAS) in Arizona is helping scientists set limits on the quantum nature of space-time on extremely tiny scales, as explained in our latest press release.
Certain aspects of quantum mechanics predict that space-time - the three dimensions of space plus time -- would not be smooth on the scale of about ten times a billionth of a trillionth of the diameter of a hydrogen atom's nucleus. They refer to the structure that may exist at this extremely small size as "space-time foam." This artist's illustration depicts how the foamy structure of space-time may appear, showing tiny bubbles quadrillions of times smaller than the nucleus of an atom that are constantly fluctuating and last for only infinitesimal fractions of a second.
Light: Beyond the Bulb at Puerto Rico
During the month of April 2015 the Chandra exhibit "Light: Beyond the Bulb" for the International Year of Light was displayed at the main library of the University of Puerto Rico (UPR) and impacted many hundreds of visitors. The exhibit was announced to the public using different media with the support of the Communications Office at the UPR. Dr. Gloria Isidro (Caribbean University) organized special talks at Caribbean University of Bayamón in which hundreds of students, faculty and staff participated (April 8th and 9th, 2015). These talks included a description of the goals of the International Year of Light 2015, announced the exhibit of images at the University of Puerto Rico during the month of April and showed a video of the "Light: Beyond the Bulb" exhibit.

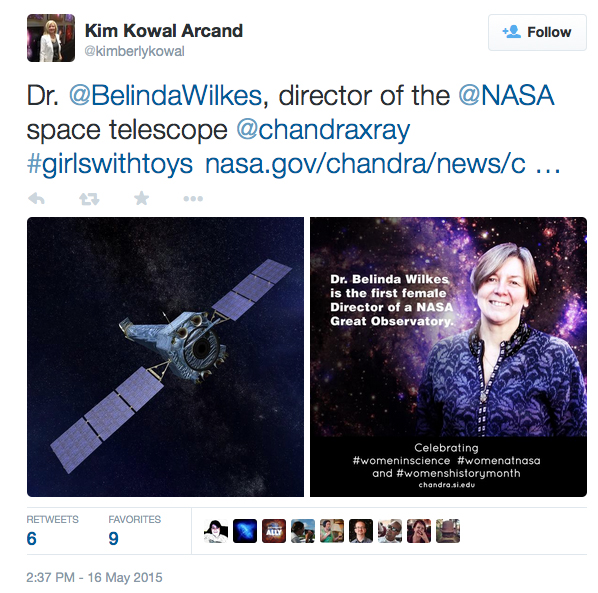
X-ray Astronomy and #girlswithtoys
There have been so many excellent images and messages being tied to the hashtag #girlswithtoys on Twitter over the past several days. We would love to be able to take some selfies with some of the many female scientists, engineers, and other professionals who use and run the Chandra X-ray Observatory. (Of course, the Director of Chandra is Belinda Wilkes, the first woman to lead one of NASA’s Great Observatories) Unfortunately, Chandra is currently in its highly elliptical orbit that takes it a third of the way to the Moon, so the spacecraft is unavailable for a snapshot.