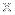Researchers using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory have found evidence that the normally dim region very close to the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy flared up with at least two luminous outbursts in the past few hundred years.
This discovery comes from a new study of rapid variations in the X-ray emission from gas clouds surrounding the supermassive black hole, a.k.a. Sagittarius A*, or Sgr A* for short. The scientists show that the most probable interpretation of these variations is that they are caused by light echoes.
The echoes from Sgr A* were likely produced when large clumps of material, possibly from a disrupted star or planet, fell into the black hole. Some of the X-rays produced by these episodes then bounced off gas clouds about thirty to a hundred light years away from the black hole, similar to how the sound from a person's voice can bounce off canyon walls. Just as echoes of sound reverberate long after the original noise was created, so too do light echoes in space replay the original event.
While light echoes from Sgr A* have been seen before in X-rays by Chandra and other observatories, this is the first time that evidence for two distinct flares has been seen within a single set of data.
More than just a cosmic parlor trick, light echoes provide astronomers an opportunity to piece together what objects like Sgr A* were doing long before there were X-ray telescopes to observe them. The X-ray echoes suggest that the area very close to Sgr A* was at least a million times brighter within the past few hundred years. X-rays from the outbursts (as viewed in Earth's time frame) that followed a straight path would have arrived at Earth at that time. However, the reflected X-rays in the light echoes took a longer path as they bounced off the gas clouds and only reached Chandra in the last few years.
A new animation shows Chandra images that have been combined from data taken between 1999 and 2011. This sequence of images, where the position of Sgr A* is marked with a cross, show how the light echoes behave. As the sequence plays, the X-ray emission appears to be moving away from the black hole in some regions. In other regions it gets dimmer or brighter, as the X-rays pass into or away from reflecting material. Note that there is a slightly smaller field of view at the end of the sequence so the apparent disappearance of emission in the top-left hand corner is not real.
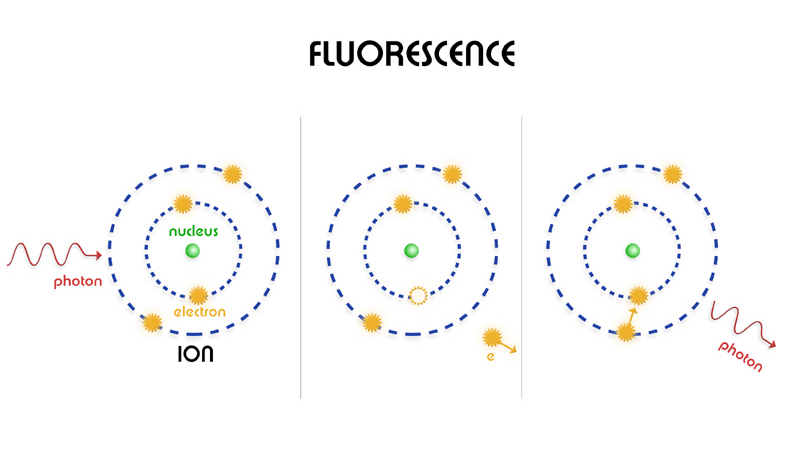
The X-ray emission shown here is from a process called fluorescence. Iron atoms in these clouds have been bombarded by X-rays, knocking out electrons close to the nucleus and causing electrons further out to fill the hole, emitting X-rays in the process. Other types of X-ray emission exist in this region but are not shown here, explaining the dark areas.
This is the first time that astronomers have seen both increasing and decreasing X-ray emission in the same structures. Because the change in X-rays lasts for only two years in one region and over ten years in others, this new study indicates that at least two separate flares were responsible for the light echoes observed from Sgr A*.
There are several possible causes of the flares: a short-lived jet produced by the partial disruption of a star by Sgr A*; the ripping apart of a planet by Sgr A*; the collection by Sgr A* of debris from close encounters between two stars; and an increase in the consumption of material by Sgr A* because of clumps in the gas ejected by massive stars orbiting Sgr A*. Further studies of the variations are needed to decide between these options.
The researchers also examined the possibility that a magnetar - a neutron star with a very strong magnetic field - recently discovered near Sgr A* might be responsible for these variations. However, this would require an outburst that is much brighter than the brightest magnetar flare ever observed.
A paper describing these results has been published in the October 2013 issue of the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics and is available online. The first author is Maïca Clavel from AstroParticule et Cosmologie (APC) in Paris, France. The co-authors are Régis Terrier and Andrea Goldwurm from APC; Mark Morris from University of California, Los Angeles, CA; Gabriele Ponti from Max-Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, Garching, Germany; Simona Soldi from APC and Guillaume Trap from Palais de la découverte - Universcience, Paris, France.
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., manages the Chandra Program for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls Chandra's science and flight operations from Cambridge, Mass.
The image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory reveals a dramatic scene at the center of the Milky Way, where the supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), resides. Sgr A* is marked by an asterisk at the middle right of the image. The region around Sgr A* is illuminated by light echoes—reflections of past outbursts from the black hole. These echoes are caused by X-rays bouncing off gas clouds light-years away, similar to how sound bounces off canyon walls. The image showcases regions where the X-ray emission, shown as blue clumps splattered to the left side, appears to move away from the black hole, dimming or brightening as the X-rays interact with the reflecting material. The image stacks 5 Chandra observations from 1999 through 2011 and shows the changes in between those times.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||