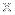This is a composite image of the northern part of the galaxy cluster Abell 1758, located about 3.2 billion light years from Earth, showing the effects of a collision between two smaller galaxy clusters. Chandra X-ray data (blue) reveals hot gas in the cluster and data from the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) in India (pink) shows huge "halos" generated by ultra-relativistic particles and magnetic fields over vast scales. Optical data from the Digitized Sky Survey are colored gold.
A study of this galaxy cluster and 31 others with Chandra and the GMRT shows that huge radio halos are generated during collisions between galaxy clusters. This result implies that galaxy clusters with radio halos are still forming, while clusters without this radio emission are not still accumulating large amounts of material. The result also implies that relativistic electrons are likely accelerated by turbulence generated by mergers between clusters
Galaxy clusters are the largest structures in the Universe that are bound together by gravity. They form when smaller clusters or groups of galaxies collide and merge. Collisions between galaxy clusters, such as this one in Abell 1758 and its more famous cousin the Bullet Cluster, are the most energetic events in the Universe since the Big Bang. Their growth rate over the last 7 billion years has been slowed by the effects of dark energy, as shown by previous studies with Chandra.
The image features a galaxy cluster named Abell 1758, which appears as a bright blue and hot pink-purple object in the center of the frame. This galaxy cluster is a conglomeration of many galaxies that are held together by their mutual gravitational attraction. The galaxy cluster is shaped like an irregularly shaped cloud, with bright points of light visible in the black background. The colors of the galaxy cluster in this image are predominantly blue and pink-purple, but there are also some small white and gold stars, galaxies and other objects visible in the background. The irregular shape of Abell 1758 is like a blurry blue tang fish draped a hot pink boa around itself. This composite image shows the effects of a collision between two smaller galaxy clusters. Chandra X-ray data (blue) reveals hot gas in the cluster and data from the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) in India (pink) shows huge "halos" generated by ultra-relativistic particles and magnetic fields over vast scales. Optical data from the Digitized Sky Survey are colored gold-white.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||