CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
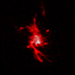
X-ray, Optical & H-alpha Images of Abell 2597
A Chandra study of over 200 galaxy clusters has helped determine how giant black holes at their centers affect the growth and evolution of their host galaxy. This study, which includes Abell 2597 shown here, revealed that an unusual form of cosmic precipitation enables a feedback loop of cooling and heating, stifling star formation in the middle of these galaxy clusters. These images of Abell 2597 show X-rays from Chandra, optical data from Hubble and the Digitized Sky Survey, and emission from hydrogen atoms from the Walter Baade Telescope in Chile.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Michigan State Univ/M.Voit et al; Optical: NASA/STScI & DSS; H-alpha: Carnegie Obs./Magellan/W.Baade Telescope/U.Maryland/M.McDonald)
A Chandra study of over 200 galaxy clusters has helped determine how giant black holes at their centers affect the growth and evolution of their host galaxy. This study, which includes Abell 2597 shown here, revealed that an unusual form of cosmic precipitation enables a feedback loop of cooling and heating, stifling star formation in the middle of these galaxy clusters. These images of Abell 2597 show X-rays from Chandra, optical data from Hubble and the Digitized Sky Survey, and emission from hydrogen atoms from the Walter Baade Telescope in Chile.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Michigan State Univ/M.Voit et al; Optical: NASA/STScI & DSS; H-alpha: Carnegie Obs./Magellan/W.Baade Telescope/U.Maryland/M.McDonald)
Return to Abell 2597 (March 3, 2015)