CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
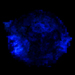
Illustration of a Star's Inner Layers
A new X-ray study of the remains of an exploded star indicates that the supernova that disrupted the massive star may have turned it inside out in the process. Using very long observations of Cassiopeia A (or Cas A), a team of scientists has mapped the distribution of elements in the supernova remnant in unprecedented detail. This information shows where the different layers of the pre-supernova star are located three hundred years after the explosion, and provides insight into the nature of the supernova. An artist's illustration shows a simplified picture of the inner layers of the star that formed Cas A just before it exploded, with the predominant concentrations of different elements represented by different colors: iron in the core (blue), overlaid by sulfur and silicon (green), then magnesium, neon and oxygen (red).
(Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss;)
A new X-ray study of the remains of an exploded star indicates that the supernova that disrupted the massive star may have turned it inside out in the process. Using very long observations of Cassiopeia A (or Cas A), a team of scientists has mapped the distribution of elements in the supernova remnant in unprecedented detail. This information shows where the different layers of the pre-supernova star are located three hundred years after the explosion, and provides insight into the nature of the supernova. An artist's illustration shows a simplified picture of the inner layers of the star that formed Cas A just before it exploded, with the predominant concentrations of different elements represented by different colors: iron in the core (blue), overlaid by sulfur and silicon (green), then magnesium, neon and oxygen (red).
(Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss;)
2
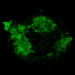
Chandra X-ray Element Map
This Chandra X-ray image uses the same color scheme as in the illustration above, to show the distribution of iron, sulfur and magnesium in the supernova remnant. The data show that the distributions of sulfur and silicon are similar, as are the distributions of magnesium and neon. Oxygen, which according to theoretical models is the most abundant element in the remnant, is difficult to detect because the X-ray emission characteristic of oxygen ions is strongly absorbed by gas in along the line of sight to Cas A, and because almost all the oxygen ions have had all their electrons stripped away.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/GSFC/U.Hwang & J.Laming)
This Chandra X-ray image uses the same color scheme as in the illustration above, to show the distribution of iron, sulfur and magnesium in the supernova remnant. The data show that the distributions of sulfur and silicon are similar, as are the distributions of magnesium and neon. Oxygen, which according to theoretical models is the most abundant element in the remnant, is difficult to detect because the X-ray emission characteristic of oxygen ions is strongly absorbed by gas in along the line of sight to Cas A, and because almost all the oxygen ions have had all their electrons stripped away.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/GSFC/U.Hwang & J.Laming)
Return to Cassiopeia A (March 29, 2012)