CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
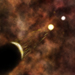
Illustration Explaining the Arc in Tycho
This is an artist's impression showing an explanation from scientists for the origin of an X-ray arc in Tycho's supernova remnant. It is believed that material was stripped off the companion star by the explosion of the white dwarf in the Type Ia supernova explosion, forming the shock wave seen in the arc. The arc has blocked debris from the explosion, creating a "shadow" behind the arc. The force of the explosion imparted a kick to the companion star, and this combined with the orbital velocity of the companion before the explosion to give the "observed" motion of the companion. Previously, studies with optical telescopes have revealed a star within the remnant that is moving much more quickly than its neighbors, showing that it could be the companion to the supernova. The size of the companion's orbit is not shown to scale here: the separation between it and the white dwarf before the explosion is estimated to have only been about a millionth of a light year, while the full scale of the illustration is over 10 light years.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss)
This is an artist's impression showing an explanation from scientists for the origin of an X-ray arc in Tycho's supernova remnant. It is believed that material was stripped off the companion star by the explosion of the white dwarf in the Type Ia supernova explosion, forming the shock wave seen in the arc. The arc has blocked debris from the explosion, creating a "shadow" behind the arc. The force of the explosion imparted a kick to the companion star, and this combined with the orbital velocity of the companion before the explosion to give the "observed" motion of the companion. Previously, studies with optical telescopes have revealed a star within the remnant that is moving much more quickly than its neighbors, showing that it could be the companion to the supernova. The size of the companion's orbit is not shown to scale here: the separation between it and the white dwarf before the explosion is estimated to have only been about a millionth of a light year, while the full scale of the illustration is over 10 light years.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss)
2
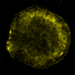
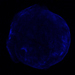
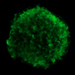
Image Showing the "Shadow" of the Arc
This image shows iron debris in Tycho's supernova remnant. The site of the supernova explosion is shown, as inferred from the motion of the possible companion to the exploded white dwarf. The position of material stripped off the companion star by the explosion, and forming an X-ray arc, is shown by the white dotted line. This structure is most easily seen in an image showing X-rays from the arc's shock wave. Finally, the arc has blocked debris from the explosion creating a "shadow" in the debris between the red dotted lines, extending from the arc to the edge of the remnant.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Chinese Academy of Sciences/F. Lu et al)
This image shows iron debris in Tycho's supernova remnant. The site of the supernova explosion is shown, as inferred from the motion of the possible companion to the exploded white dwarf. The position of material stripped off the companion star by the explosion, and forming an X-ray arc, is shown by the white dotted line. This structure is most easily seen in an image showing X-rays from the arc's shock wave. Finally, the arc has blocked debris from the explosion creating a "shadow" in the debris between the red dotted lines, extending from the arc to the edge of the remnant.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Chinese Academy of Sciences/F. Lu et al)
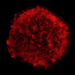
3
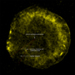
X-ray Images of Tycho's Supernova Remnant
This Chandra image of the Tycho supernova remnant contains new evidence for what triggered the original supernova explosion. Tycho was formed by a Type Ia supernova, a category of stellar explosion used in measuring astronomical distances because of their reliable brightness. In the lower left region of Tycho is a blue arc of X-ray emission. Several lines of evidence support the conclusion that this arc is due to a shock wave created when a white dwarf exploded and blew material off the surface of a nearby companion star. This supports one popular scenario for the trigger of a Type Ia supernova. Understanding the origin of Type Ia supernovas is important because they have been used to determine that the Universe is expanding at an accelerating rate.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Chinese Academy of Sciences/F. Lu et al)
This Chandra image of the Tycho supernova remnant contains new evidence for what triggered the original supernova explosion. Tycho was formed by a Type Ia supernova, a category of stellar explosion used in measuring astronomical distances because of their reliable brightness. In the lower left region of Tycho is a blue arc of X-ray emission. Several lines of evidence support the conclusion that this arc is due to a shock wave created when a white dwarf exploded and blew material off the surface of a nearby companion star. This supports one popular scenario for the trigger of a Type Ia supernova. Understanding the origin of Type Ia supernovas is important because they have been used to determine that the Universe is expanding at an accelerating rate.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Chinese Academy of Sciences/F. Lu et al)
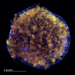
4
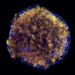
Tycho's Supernova Remnant with Scale Bar
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Chinese Academy of Sciences/F. Lu et al
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Chinese Academy of Sciences/F. Lu et al
Tycho's Supernova Remnant (April 26, 2011)