Chandra Reveals a Compact Nebula Created by a Shooting Neutron Star
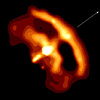
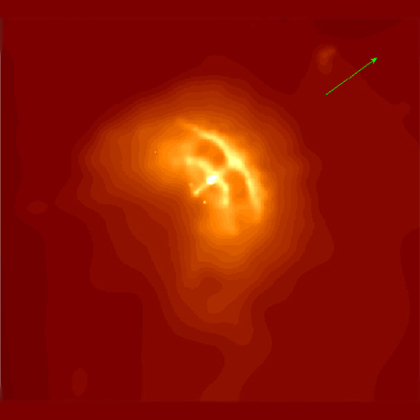
Chandra image of compact nebula around Vela pulsar. The image shows a dramatic bow-like structure at the leading edge of the cloud, or nebula, embedded in the Vela supernova remnant. This bow and the smaller one inside it, are thought to be the near edges of tilted rings of X-ray emission from high-energy particles produced by the central neutron star. Perpendicular to the bows are jets that emanate from the central pulsar, or neutron star. As indicated by the green arrow, the jets point in the same direction as the motion of the pulsar. The swept back appearance of the nebula is due to the motion of the pulsar through the supernova remnant.
The rings are thought to represent shock waves due to matter rushing away from the neutron star. More focused flows at the neutron star's polar regions produce the jets. The origin of this activity is thought to be enormous electric fields caused by the combination of the rapid rotation and intense magnetic fields of the neutron star.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
This Chandra X-ray Observatory image shows a bright orange-yellow compact nebula around the Vela pulsar. The image has a large, dramatic bow-like structure at the leading edge of the cloud, or nebula, embedded in the Vela supernova remnant. This larger bow and a smaller one just inside it, are thought to be the near edges of tilted rings of X-ray emission from high-energy particles produced by the central neutron star. Perpendicular to the two bows are jets that emanate from the central pulsar, or neutron star. As indicated by a green arrow in the upper right at about 2 o'clock, the jets point in the same direction as the motion of the pulsar. The swept back appearance of the nebula is due to the motion of the pulsar through the supernova remnant. The bright orange-yellow rings are thought to represent shock waves due to matter rushing away from the neutron star. More focused flows at the neutron star's polar regions produce the jets.