Chandra Discovers X-ray Source at the Center of Our Galaxy
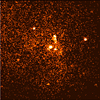
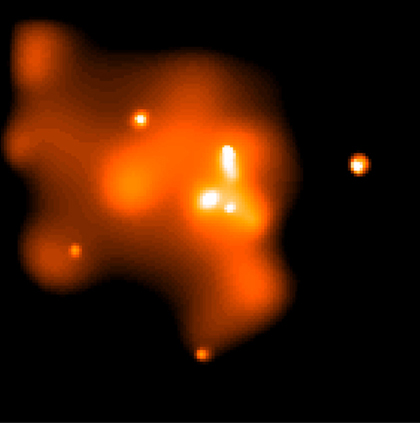
Chandra X-ray image of the innermost 10 light years at the center of our galaxy. The image has been smoothed to bring out the X-ray emission from an extended cloud of hot gas surrounding the supermassive black-hole candidate Sagittarius A* (larger white dot at the very center of the image- a little to the left and above the smallest white dot). This gas glows in X-ray light because it has been heated to a temperature of millions of degrees by shock waves produced by supernova explosions and perhaps by colliding winds from young massive stars.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
The X-ray image of the supermassive black-hole candidate Sagittarius A* features a bright, glowing object in the center of a dark background. The object appears to be shaped like a bulbous form, and it is surrounded by smaller, brighter dots that seem to be clustered around the center. This Chandra X-ray Observatory image of the innermost 10 light years at the center of our galaxy has been smoothed to bring out the X-ray emission from an extended cloud of hot gas surrounding the supermassive black-hole Sagittarius A* (the larger white dot at the very center of the image- a little to the left and above the smallest white dot). This gas glows in X-ray light because it has been heated to a temperature of millions of degrees by shock waves produced by supernova explosions and perhaps by colliding winds from young massive stars.