Roasted and Shredded by a Stellar Sidekick
White Dwarf KPD 0005+5106
Credit: Illustration: NASA/CXC/M. Weiss; X-ray (Inset): NASA/CXC/ASIAA/Y.-H. Chu, et al.
A team of scientists used NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and ESA's XMM-Newton to investigate some unusual X-ray activity of a white dwarf star, as reported in our latest press release. The data suggest this white dwarf is blasting a companion object, which is either a low-mass star or planet, with waves of heat and radiation while pulling it apart through gravitational force.
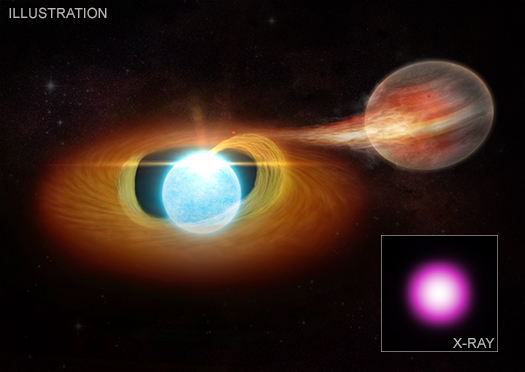
Most stars, including the Sun, will become "white dwarfs" after they begin to run out of fuel, expand and cool into a red giant, and then lose their outer layers. This evolution leaves behind a stellar nub that slowly fades for billions of years. An artist's illustration shows a white dwarf as the blue-white sphere near the center.
Astronomers have observed that the white dwarf KPD 0005+5106, located about 1,300 light years from Earth, emits high-energy X-ray emission that regularly increases and decreases in X-ray brightness every 4.7 hours. This recurring ebb and flow of X-rays indicates that KPD 0005+5106 has an object in orbit around it — either a very low mass star or a planet — depicted in the illustration by the brown and red object on the right-hand side. The white dwarf pulls the material from the companion into a disk around itself, which the artist shows in orange, before it slams into its north and south poles.
The concentration of material hitting the white dwarf's poles is creating two bright spots of high-energy X-ray emission. As the white dwarf and its companion orbit around each other the hot spot facing more towards Earth would go in and out of view, causing the high-energy X-rays to regularly increase and decrease that Chandra observed.
The researchers looked at what would happen if this object was a planet with the mass about that of Jupiter, a possibility that agrees with the data more readily than a dim star or a brown dwarf. In their models, the white dwarf would pull material from the planet onto the white dwarf, a process that the planet could only survive for a few hundred million years before eventually being destroyed. This stolen material swirls around the white dwarf, which glows in X-rays that Chandra can detect.
A paper describing these results appeared in The Astrophysical Journal in April 2021 and a preprint is available online. The authors of the paper are You-Hua Chu (Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica in Taiwan), Jesús Toala (National Autonomous University of Mexico), Martín Guerrero and Florian Bauer (The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia in Spain), and Jana Bilikova and Robert Gruendel (University of Illinois, Urbana).
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
